Important Point
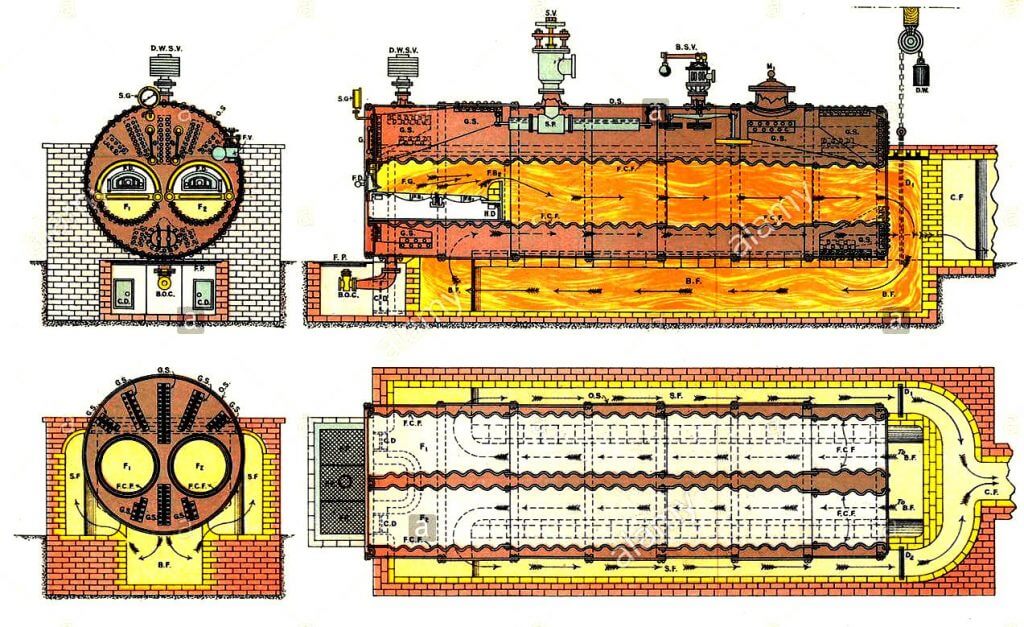
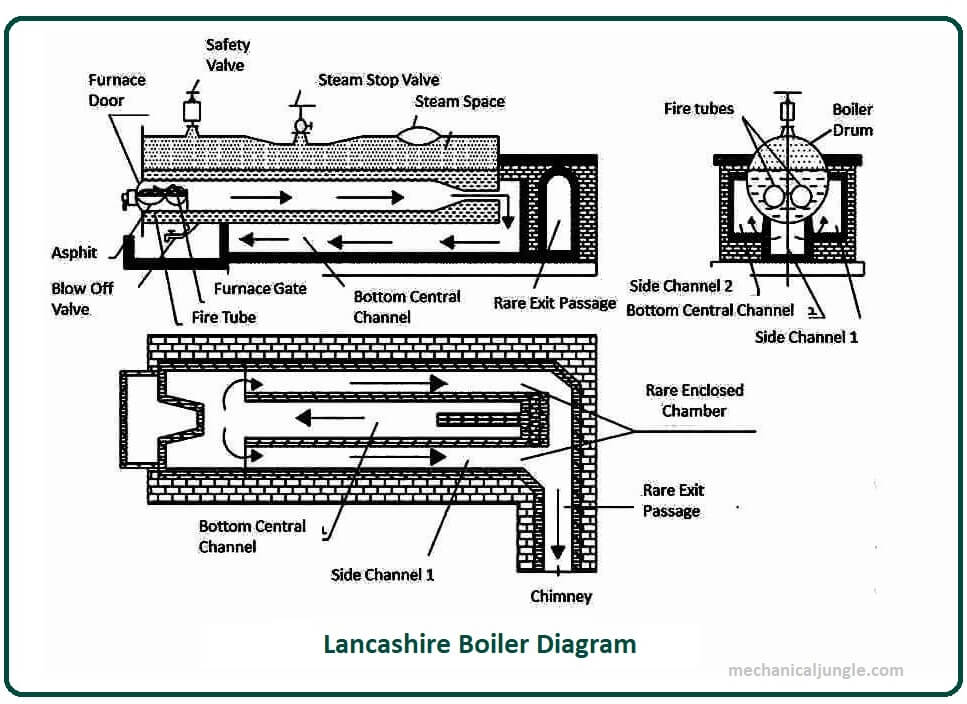
Lancashire Boiler
Today we learn about the Lancashire boiler. The most common boiler is the Sugrananda cotton industry. Lancashire is a horizontal, stationary fire tube boiler.
This boiler was invented by Sir William Fairbairn in the year 1844. Influenza gases flow through a fire tube, which is located inside the boiler shell, so it is a fire tube boiler. This boiler generation pressure steam. It is an internally fired boiler because the furnace is placed inside the boiler.
Lancashire Boiler Diagram
Also, Read: How Do Aircraft Brakes Work | How Aircraft Brakes Work | Brake Design | Aircraft Brakes
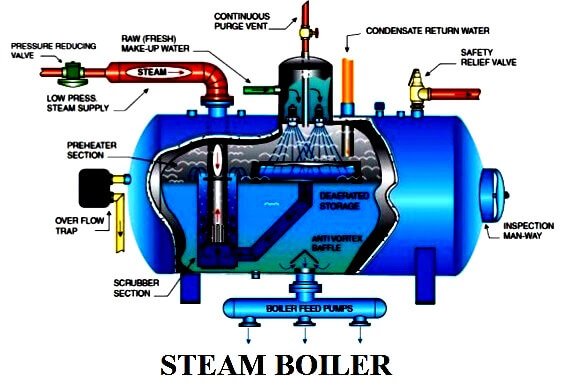
Steam Boiler Working Principle
- The basic working principle of the boiler is very simple and easy to understand.
- The boiler is essentially a closed vessel inside which water is stored. The fuel (usually coal) is burned in a furnace, and hot gases are produced.
- These hot gases come into contact with the water vessel where the heat of these hot gases is transferred to the water, and as a result, steam is produced in the boiler.
- This steam is then transported to the turbine of the thermal power plant. Many different types of boilers are used for various purposes, such as running a production unit, cleaning certain areas, sterilizing equipment, heating the surroundings, and so on.
Steam Boiler Parts And Function
The main components of the boiler consist of the furnace, membrane walls, boiler shell, economizer, cyclone, water storage tank, deaerator, coal bunker, hopper, conveyor, and chimney.
The following will be discussed one by one:
- Furnace
- Membrane Wall
- Shell Boilers
- Economizer
- Cyclone
- Water Storage Tank and Deaerator
- Coal Bunker
- Hopper
- Conveyor
Also, Read: Difference Between Orthogonal and Oblique Cutting | Orthogonal Machining
#1. Furnace
- A furnace or also called a furnace is a device used for heating.
- The name comes from the Latin Fornax, which means the same as the oven. Sometimes people also refer to kilns.
- The process of heat transfer in a furnace occurs in three ways:
- Heat transfer by conduction, heat flows through the conductor from the side of the pipe, which receives heat into the side of the pipe, which gives heat to the water.
#2. Membrane Wall
- The wall consists of tubes/pipes that are joined by a membrane, therefore called the membrane wall. Inside the Membranewall flows water to be boiled.
- Tube/pipe construction is from the bottom up where the bottom of the pipe is filled with heavier water mass, and it is expected that at the top, it has become steam through a combustion process where lighter mass steam will rise to the top naturally.
- The membrane wall has two headers on the bottom that serve to channel water from downcomers are pipes that connect the steam drum to the bottom of the low header.
- To prevent the spread of heat and to minimize contact with humans, the outer side of the membrane wall is mounted on an insulating wall made of rock wool wire blankets.
#3. Shell Boilers
- The boiler shell in the picture above is the type of fire tube. In a firetube boiler, hot gas passes through the pipes, and boiler feedwater is in the shell to be turned into steam.
The function of the Boiler Is:
- Collect water to be heated in the vapour pipes ( membrane wall ) and collect steam from the membrane wall and tube bundle before it flows to the factory or production room.
- Separating steam and water that results from heating in the combustion chamber (Furnace ).
- Regulate water quality by removing dissolved impurities in the boiler through continuous blowdown.
- Adjust the water level so that there is no shortage of water when the boiler is operating because if there is a lack of water, it can cause overheating of the pipe.
- The water level of the drum must always be kept at a fixed height so that the amount of fill water entering the boiler is proportional to the amount of steam leaving the boiler so that the water level can be constant.
#4. Economizer
- Economizer absorbs heat from combustion gases after passing through the boiler to heat the filler water before entering the boiler.
- The heat given to water is in the form of sensible heat (heat that causes an increase in temperature but the phase/form does not change).
- This water heating is done so that the temperature difference between the fill water and the water in the boiler is not too far away, so there is no thermal stress (the voltage caused by heating) in the boiler.
- In addition, utilizing combustion residuals will increase the efficiency of the boiler and the process of forming steam faster.
- Economizer in the form of water pipes installed in the place through which the combustion gas.
- The heat transfer that occurs in the economizer occurs in the opposite direction of the flow of the two fluids ( counterflow ).
- Boiler drum filler water flows upward toward the boiler while heating air flows downward.
#5. Cyclone
- Cyclone is a dust collector that uses the principle of centrifugal force to separate dust particles from the air based on differences in masses of air and particulates.
Components in the Cyclone Consist Of:
- The working principle of the cyclone is as follows:
- Particles from the flue gas are separated by making centrifugal force.
- Flue gas contains a lot of dust particles into the cyclone inlet and rotated in the cyclone cone with the aim of separating dust particles and air using the principle of weight difference.
- Dust particles heavier than air will fall and fall into the dust bin.
Cyclone Performance Is Very Much Influenced by :
- The particle size, because according to the stroke law states that the particle diameter el is directly proportional to the terminal setting velocity so that the greater the particle size, the cyclone efficiency will increase.
- The smaller the diameter of the cyclone cone, the higher the efficiency.
- S making large viscosity of the efficiency of the cyclone is getting smaller.
#6. Water Storage Tank and Deaerator
- The water storage tank is a device used to collect water from the water sooner to the boiler; in addition to storing water, preheating also occurs here before it is heated again in the economizer.
- The heat source is taken through the steam injection line pipe, and the temperature in the water storage tank can reach more than100 C.
- The water storage tank is also equipped with a level gauge to see the level of water inside and also equipped with sensors.
- Deaerator is a tank that serves to separate oxygen from water because O levels are too high in the air softeners can cause corrosion in pipes in boilers and other supporting pipes.
- Deaerator works based on the nature of oxygen, whose solubility in water will decrease with an increase in temperature.
#7. Coal Bunker
- Coal bunkers are the final storage places for coal, which are stored in bunkers (silos) before being used as fuel.
- The coal bunker is given a height detection device or level indicator so that when the coal bunker is full, automatically, the coal entering the coal bunker through the conveyor will stop.
#8. Hopper
- A hopper is a fuel storage device such as a silo but has a diameter that is generally larger than a silo.
- This storage device is usually made of carbon steel, where the bottom is cone-shaped to minimize the point of dispensing coal; right below it, there is a conveyor to move from the hopper to the coal bunker.
#9. Conveyor
- A conveyor is a device used to move goods from one place to another.
- C conveyor is usually used to move the goods that are continuous and sustainable; in this case, move barbara from the hopper to the coal bunker.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Lancashire Boiler
Today we learn about the Lancashire boiler. The most common boiler is the Sugrananda cotton industry. Lancashire boiler is a horizontal type and stationary fire tube boiler.
This boiler was invented by William Fairbairn in the year 1844. It is an internally fired boiler as the furnace uses to project the inside of the boiler. This boiler generates low-pressure steam and is a natural circulation boiler.
Steam Boiler Working Principle
The basic working principle of the boiler is very very simple and easy to understand. The boiler is essentially a closed vessel inside which water is stored. These hot gasses come in contact with water vessels where the heat of these hot gases transfer to the water and consequently steam is produced in the boiler
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –
- Parts of Disc Brakes
- Types of Drum Brakes
- What Is a Comparator | Types of Comparators
- How Do Aircraft Brakes Work | How Aircraft Brakes Work | Brake Design | Aircraft Brakes
- What Is Forming | Types of Forming | Forming Process in Manufacturing | Metal Forming Processes | Forming Operations
- What Is Boiler? | Types of Boiler | Steam Boiler | How Boiler Work | Boiler Operation | Boilers Diagram | How Does a Steam Boiler Work
- What Is Sigma Comparator | Construction of Sigma Comparator | Applications of Sigma Comparator | Advantages of Sigma Comparator | Disadvantages of Sigma Comparator