Important Point
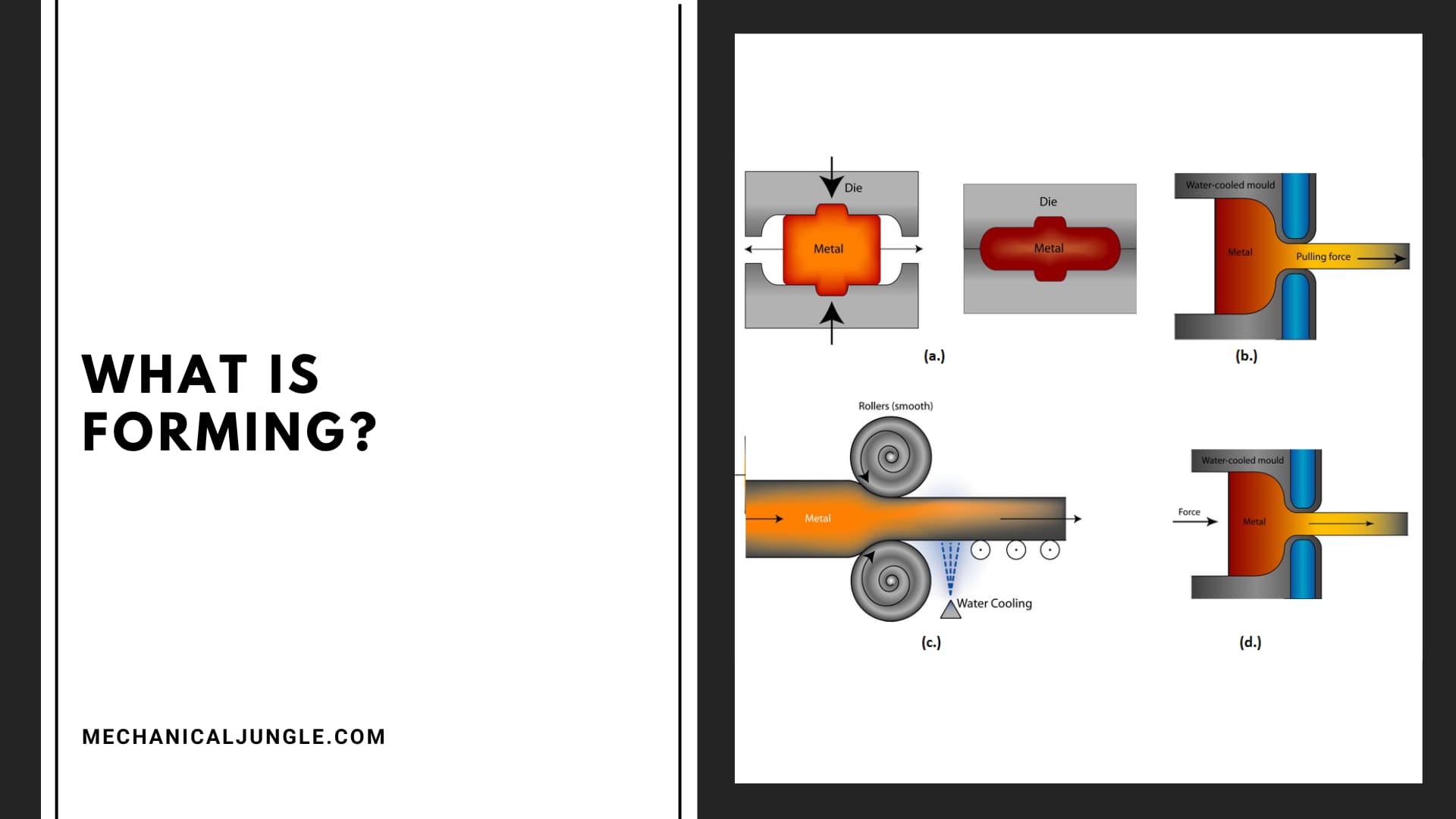
What is Forming?
Fabrication is a mechanical process used in manufacturing industries in which materials (mostly metals) undergo plastic deformation and obtain the shapes and sizes required by the application of appropriate stresses, such as compression, shear, and tension.
In the process of making, no material is removed; It is completely displaced and deformed to the required shape. Some of the processes commonly used in the manufacturing industry are:
- Forging
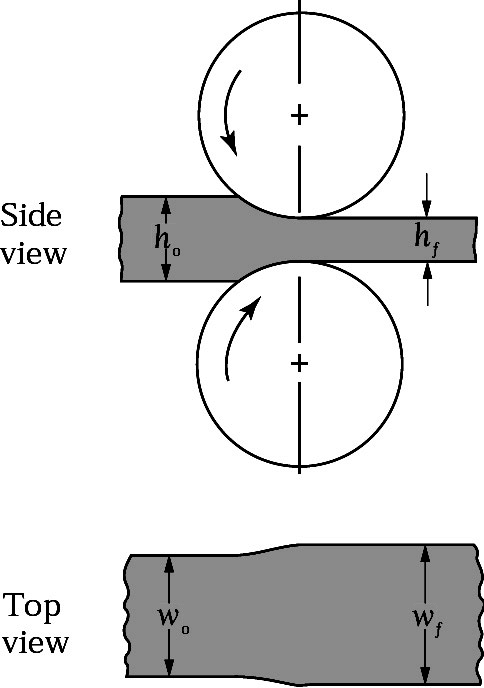
- Rolling
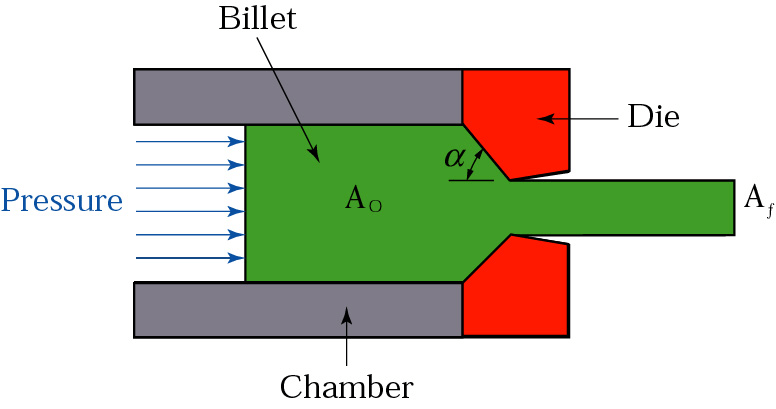
- Extrusion
- Thread rolling
- Rotary swaging
- Explosive forming
- Electromagnetic forming
Types of Forming
In the last few years, there has been a considerable increase in the adoption of automated machine tools, with increasing investment in the industrial manufacturing sector.
Not only will productivity increase, but automation of manufacturing processes helps professionals to be quite efficient and flexible during emergencies and also helps prioritize overall workflows.
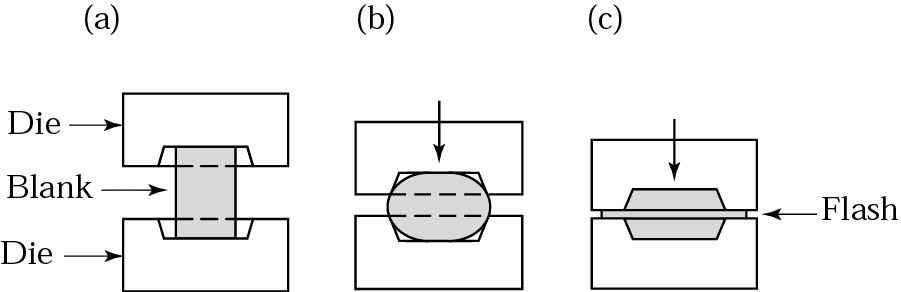
- Closed/impression die forging
- Electro-upsetting
- Forward extrusion
- Backward extrusion
- Radial forging
- Hobbing
- Isothermal forging
- Open-die forging
- Upsetting
- Nosing
- Coining
Commonly used materials include
- Ferrous materials: low carbon steels
- Nonferrous materials: copper, aluminum, and their alloys
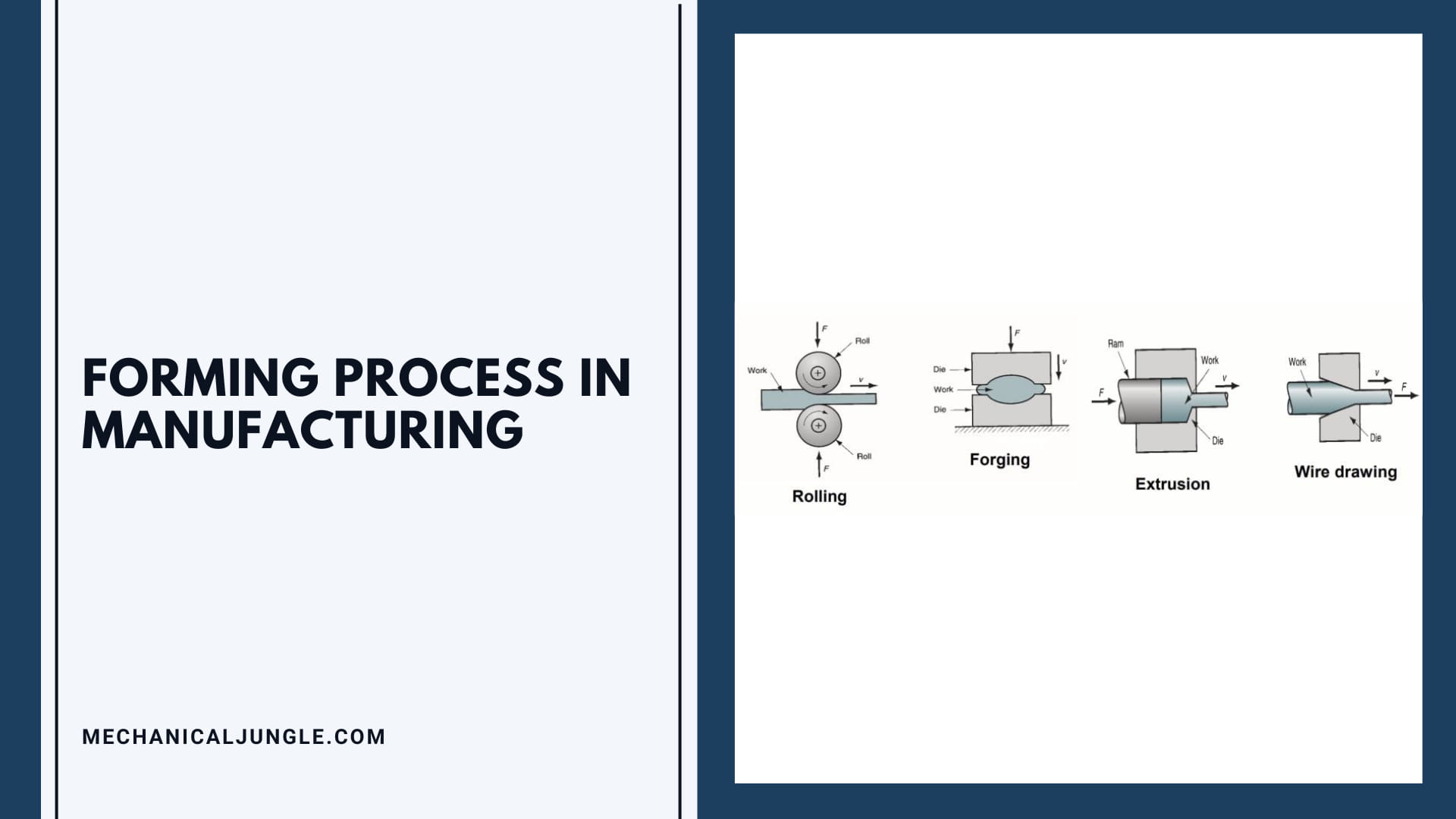
Forming Process in Manufacturing
- Production includes all types of manufacturing processes.
- There are many methods of manufacturing, such as metal casting, metal fabrication, metal machining, metal joining, and finishing.
- Due to the increasing adoption of robotics and automated equipment, the market development of the metal forming machine process is expected to grow positively in the coming years, in particular, in the manufacturing sector.
- Manufacturing companies can manage high-quality processes because automation removes the scope of human error and affects the overall quality of production.
- The market for metal forming machine processes is currently marginally fragmented due to the presence of metal forming machine tool manufacturers bringing advanced technologies to offer better products for end-user industries.
- A complete analysis of the competitive landscape of the market and information on products offered by companies will help customers to identify new competitive opportunities and to design new growth strategies to improve market shares in this competitive environment.
- Metal forming and machining are two major methods to convert raw materials into a product. Changing the shape of a material by permanent plastic deformation is best defined as metal forming.
- The only advantage of the metals forming process is that there will be no dissipation of raw materials, faster production rates, and better mechanical properties of the product.
Also, Read: What Is a Comparator | Types of Comparators
Metal Forming Processes
- Metal Fabrication: Large set of manufacturing processes in which materials are deformed To take the shape of fast die geometry. Equipment used for such deformation, Depending on the type of process, dye, punch, etc., is called.
- Plastic Deformation: the stress is beyond the yield strength of the workpiece material they wanted.
- Categories: Wholesale Metal Forming, Sheet Metal Forming.
Forming Operations
- Fine farming begins with an intermediate part constructed by casting, forging, or stamping. This process prepares the firearms component for final surface finishing and assembly.
- The majority of the operations of these metals fall under the general subject of machining. Machining describes every operation in which a dynamic tool removes metal to achieve final dimensions. In machining, a sharp metal tool or abrasive surface is refined and reduces the intermediate part to the desired form and dimensions.
- The surface of the tool should be harder than the size.
- The machining operation produces heat, which, if not controlled, will destroy the expensive tooling and potentially damage the intermediate part.
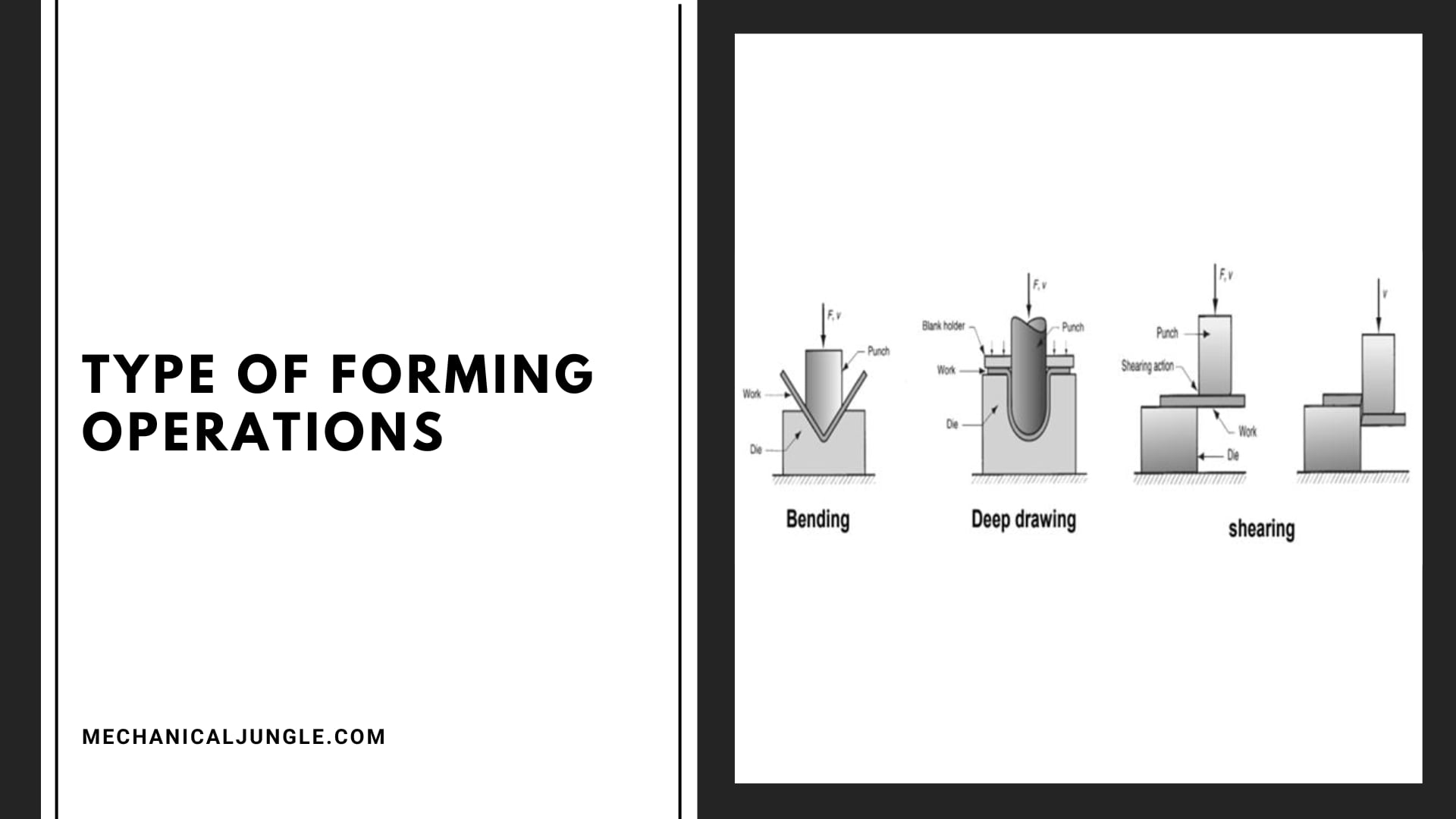
Type of Forming Operations
The type of Forming Operations is as follows
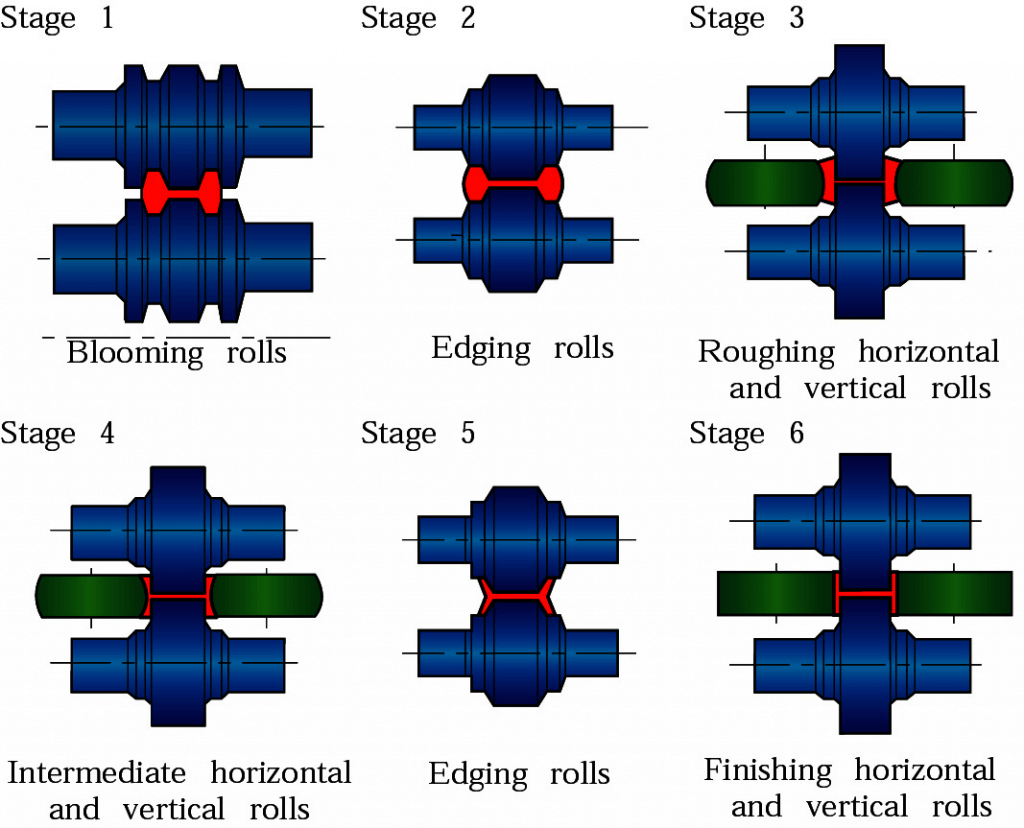
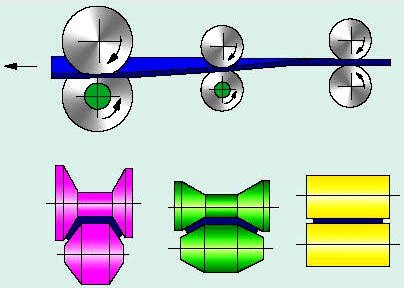
- Rolling
- Forging
- Extrusion
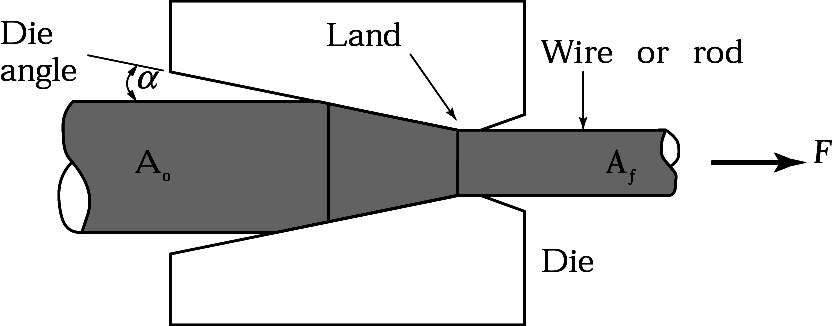
- Wire Drawing
- Roll forming
- Roll Forming
#1. Rolling:
Makes sheet metal (hot or cold)
#2. Forging:
Makes strong solid parts (hot or cold)
#3. Extrusion:
Makes complex cross-sections from soft metals and plastics (hot)
#4. Wire Drawing:
Makes a strong small dia. Wire (hot or cold)
#5. Roll Forming (Hot):
Moves bulk metal, makes I-beams
#6. Roll Forming (Cold):
Bends sheet metal into complex cross-sections
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Sheet Metal Forming Processes
When making sheet metals, however, companies often use one or more of the following forming processes.
- Curling:- Curling is a sheet metal forming process that’s used to smooth out the otherwise sharp & rugged edges of sheet metal.
- Bending:- Another common sheet metal forming process is bending. Companies typically perform bending on sheets of metal using either a brake press or a similar machine press.
- Ironing:-Sheet metal may as well be ironed to achieve a uniform thickness. Most aluminum can, for instance, is made of ironed aluminum.
- Laser Cutting:- Laser cutting has become an increasingly common sheet metal forming process in recent years. With laser cutting, sheet metals are exposed to a high-powered laser that burns holes in the metal.
- Hydroforming:- A lesser-known sheet metal forming process is hydroforming. Like deep drawing, hydroforming involves stretching blanks over a die.
- Punching:-Finally, punching is a sheet metal forming process that involves the use of a punch & dies set to create holes in sheet metal. Sheets metal is placed between the punch & die.
Sheet Metal Processes
When making sheet metals, however, companies often use one or more of the following forming processes.
- Curling:
- Bending:
- Ironing:
- Laser Cutting:
- Hydroforming:
- Punching:
Sheet Metal Forming
Sheet metal forming is a process where pieces of sheet metal are modified to their geometry rather than removing any materials. The applied process generates a force that stresses the material to deform. This in turn gives the possibility to bend och stretch the sheet to a variety of complex shapes.
Forming Metal
Metal forming is a fabrication process that creates structural parts and components out of metal sheets or tubing. A basic metal forming process will bend or deform a metal workpiece to a desired geometric shape.
Metal Forming Techniques
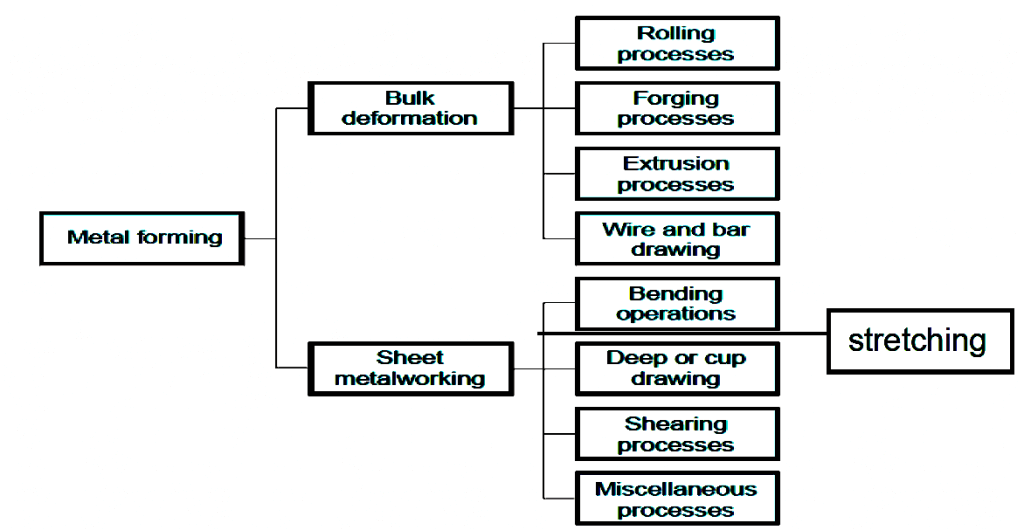
Typically, metal forming processes can be classified into two broad groups. One is bulk-forming and the other is sheet metal forming. Bulk deformation refers to the use of raw materials for forming which have a low surface area to volume ratio. Rolling, forging, extrusion, and drawing are bulk forming processes.
Metal Forming
Metal forming is a process where materials are subjected to plastic deformation to obtain the required size, shape, and/or change the physical and chemical properties. Metal forming is divided into two groups, bulk-forming, and sheet forming.
Forming Process
Forming is a mechanical process used in manufacturing industries wherein materials (mostly metals) undergo plastic deformations and acquire required shapes and sizes by application of suitable stresses such as compression, shear, and tension.
What Is Metal Forming?
Forming, also known as “metal forming,” includes a wide range of manufacturing processes in which metal is deformed into a required shape by the application of suitable stresses. To make the metal plastically deformed, forces must be applied that are greater than the yield strength of the metals.
What Is Forming?
general, “forming” refers to the act of shaping or creating something. It involves the transformation of a material or substance into a desired shape, structure, or form. For example, in manufacturing, forming may involve processes like casting, forging, molding, or bending, where raw materials are manipulated to obtain specific shapes or products.
In the context of psychology and group dynamics, “forming” is one of the stages in the development of a team or group. It is the initial stage where individuals come together, establish their roles and relationships, and begin to form a cohesive unit. This stage is characterized by orientation, getting to know one another, and setting the foundation for future interactions.
In the context of the Tuckman’s stages of group development model, “forming” is the first stage, followed by storming, norming, and performing. This model describes the natural progression and challenges that groups typically experience as they develop and work towards achieving their goals.
“Forming” can also refer to the process of creating or filling out a form, such as a document or application. It involves providing information, answering questions, and completing the necessary fields or sections.
Forming Process in Sheet Metal
Sheet metal forming includes treatments such as bending, spinning, drawing, or stretching implemented by dies or punching tools. Forming is mostly performed on a press and parts are formed between two dies.
Metal Forming Process
Metal forming is a primary manufacturing process that includes drawing, forging, rolling, and bending. Ultrasonic metal forming is the application of ultrasonic vibrations to these processes to enhance performance through increased production speeds, less tool wear, reduced forming forces, and better surface finish.
What Is Forming Process?
The forming process refers to a set of manufacturing techniques used to shape materials into specific geometries or forms. It involves the transformation of raw materials into desired shapes or structures by applying mechanical forces, heat, or a combination of both. The forming process is commonly used in various industries, including manufacturing, construction, automotive, aerospace, and more.
Forming Manufacturing Process
- rolling, where the material passes through a pair of rolls,
- extrusion, where machine push the material through an orifice,
- die forming, where a press stamps the material around or onto a die,
- forging, where localized compressive forces shape the material.
Types of Forming Process
There are four types of forming processes: forging, rolling, extruding, and drawing. I like to refer to these as pounding, rolling, pushing, and pulling. Hopefully, by the end of this section, you will understand why I use those terms. Blacksmiths have been hammering (pounding) metals into shape for some time.
Following Is an Example of Metal Forming Process
Some popular metal forming processes are forging, rolling, wire drawing, extrusion, deep drawing, and bending.
Types of Metal Forming Process
There are several types of metal forming processes, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. Here are some common types of metal forming processes:
- Rolling: Rolling is a process that involves passing a metal through a set of rollers to reduce its thickness or change its shape. It is commonly used to produce sheets, plates, and foils.
- Extrusion: Extrusion is a process where a metal is forced through a die to create a continuous profile with a fixed cross-section. This process is commonly used to produce long, cylindrical shapes such as rods, tubes, and structural components.
- Forging: Forging involves shaping a metal by applying compressive forces using hammers, presses, or dies. This process can be done either through hot forging (heating the metal) or cold forging (forming at room temperature). Forging is used to produce strong and durable components like gears, crankshafts, and connecting rods.
- Stamping: Stamping is a process where a flat sheet of metal is formed into a specific shape or contour using a press and a die. It is commonly used in mass production to create parts such as car body panels, appliance casings, and metal furniture.
- Drawing: Drawing is a metal forming process where a flat sheet or wire is pulled through a die to reduce its cross-section while increasing its length. It is commonly used to produce wires, tubes, and seamless pipes.
- Bending: Bending involves deforming a metal sheet or bar to form angles or curves. It is often used to create components such as brackets, frames, and enclosures.
- Deep Drawing: Deep drawing is a specialized form of sheet metal forming where a flat sheet is drawn into a three-dimensional shape, such as a cup or container, using a die and a punch.
Example of Metal Forming Process
Some of the more common processes are bending, stretching, deep drawing, and roll forming. Bending is a flexible metal forming process, bending utilizes a brake press or similar type of press machine. The metal sheet is formed by placing it over a die block that punch-presses the material.
Forming Manufacturing
Forming is a mechanical process used in manufacturing industries wherein materials (mostly metals) undergo plastic deformations and acquire required shapes and sizes by application of suitable stresses such as compression, shear and tension.
What Is Forming in Manufacturing Process?
In metalworking, forming is the fashioning of metal parts and objects through mechanical deformation; the workpiece is reshaped without adding or removing material, and its mass remains unchanged.
Metal Working Processes
- Forging. Forging is a common practice for intricate metalwork.
- Casting. Whereas forging metal is something that’s done by hand, casting is the process of pouring molten metal into a mold.
- Drawing.
- Forming.
- Machining.
- Extrusion.
- Cutting.
- Punching.
Metal Manufacturing Processes
Metal manufacturing processes encompass a wide range of techniques used to produce metal components, structures, or products. Here are some common metal manufacturing processes:
- Casting: Casting involves pouring molten metal into a mold and allowing it to solidify to obtain a desired shape. It is used to produce complex shapes or parts with intricate details. Casting processes include sand casting, investment casting, die casting, and continuous casting.
- Machining: Machining is a subtractive manufacturing process that involves removing material from a metal workpiece using cutting tools. Common machining processes include milling, turning, drilling, grinding, and threading. These processes are used to achieve precise dimensions, surface finishes, and complex shapes.
- Forming: Forming processes reshape metal materials without removing material. This includes techniques such as rolling, extrusion, forging, stamping, bending, and deep drawing, which were discussed in the previous response.
- Welding: Welding joins metal parts together by melting and fusing them. It is commonly used in structural fabrication, construction, and automotive industries. Welding processes include arc welding, gas welding, resistance welding, and laser welding.
- Powder Metallurgy: Powder metallurgy involves compacting fine metal powders into a desired shape and then sintering them to bond the particles. It is used to produce complex shapes, porous structures, and components with specific properties. Powder metallurgy processes include powder compaction, sintering, and post-processing operations.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): Additive manufacturing processes build metal objects layer by layer using computer-controlled systems. Metal 3D printing enables the production of intricate geometries, customization, and reduced material waste. Common metal additive manufacturing techniques include selective laser melting (SLM), electron beam melting (EBM), and binder jetting.
- Heat Treatment: Heat treatment processes involve subjecting metal parts to controlled heating and cooling cycles to alter their properties. This includes processes like annealing, quenching, tempering, and case hardening. Heat treatment enhances metal strength, hardness, toughness, and ductility.
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –
- Ultrasonic Milling
- Chemical Milling Process
- How Do Aircraft Brakes Work | How Aircraft Brakes Work | Brake Design | Aircraft Brakes
- Lancashire Boiler | Lancashire Boiler Diagram | Steam Boiler Working Principle | Steam Boiler Parts And Function
- What Is Boiler? | Types of Boiler | Steam Boiler | How Boiler Work | Boiler Operation | Boilers Diagram | How Does a Steam Boiler Work
- Difference Between Air Conditioning and Refrigeration Why We Need a Refrigeration | Refrigeration System | Refrigeration Cycle | Principle of Refrigeration
- What Is Sigma Comparator | Construction of Sigma Comparator | Applications of Sigma Comparator | Advantages of Sigma Comparator | Disadvantages of Sigma Comparator