Important Point
What Is Spring in Mechanical?
Spring are mechanical devices that pull, push, wind, support, lift, or protect. They are mainly used to provide force in mechanical assemblies – compressive, tensile, or torsion – where they can be used to lift engine valves, open die sets, or hold batteries, just to name a few examples. Springs are usually wound with wire but can be made of solid steel, manufactured as cylinders, formed as bags, sealed with steel, or assembled from other springs.
Ordinary wire springs exhibit force whose magnitude increases linearly as the spring is pushed, pulled, or twisted. Mechanical springs are a device that can also be defined as an elastic or flexible member whose main functions are to deflect under the action of the load and fix its original shape when the load is removed.
It is also used for storing energy. Today we learn about the types of springs used for various purposes in mechanical. The spring is an elastic machine element that can deflect under the application of a load. When the loads are removed, it regains their original position.
In other words, a spring is a mechanical object made of a material with a very high yield strength to restore elasticity. It is used to absorb shocks in various machines, or it is also designed to transfer shocks and vibrations on various critical machine members.
Also, Read: Parts and Functions of Grinding Machine | Grinding Machine | Grinding Machine Types
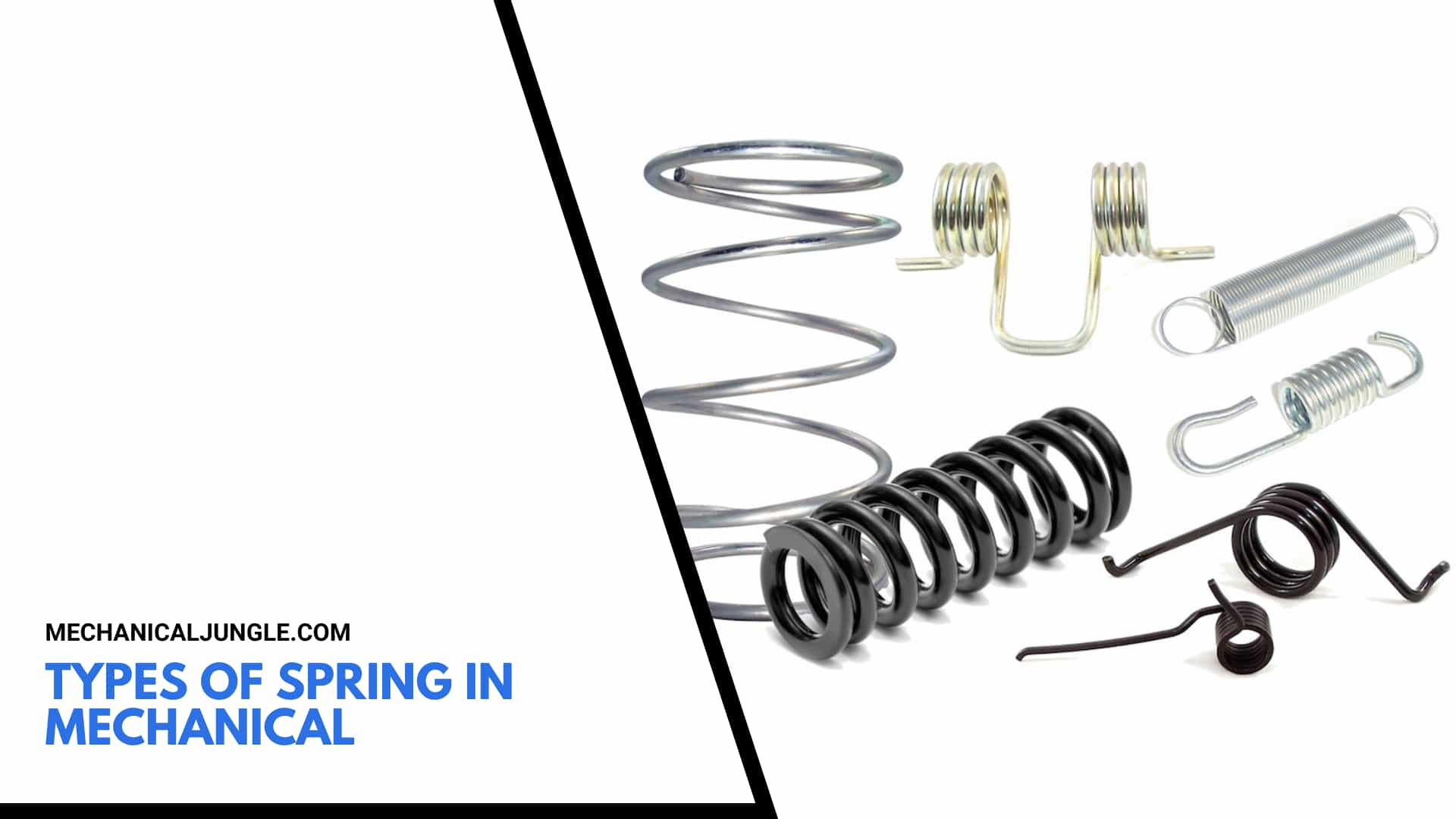
Types of Spring in Mechanical:
#1. Compression Springs
Compressed springs are helically coiled wires that are designed to provide compressive force. Under increasing load, the space between the coils closes until the compressed length of the spring is reached when the coils touch. The main specifications include spring rate, helix type, spring end type, wire diameter, material, different diameter, and free length.
Compression springs are mainly used in manufacturing applications, where a variable and opposing force is required between components. The ends may be open (left as cut) or closed (where the last coil is flattened against the adjacent coil to produce a square end relative to the axis).
Increasing the ends can also be achieved by grinding the surface of the final coil. Compression springs, while generally fashioned from wire, can also be made specifically for demanding applications.
#2. Torsion Springs
Torsion springs are helical, or flat spirals coil or strips used to apply or resist torque loads. Key specifications include spring rate, spring end type, wire diameter, material, and torque rating in a known position.
Torsion springs are mainly used in manufacturings applications as components for various motion control. They come in two basics types, helical or (coils) torsion springs, like compression or expansion springs, and act in radial directions in applying torque axially to produce tension or compression, and spiral torsion springs. , As the concentric spiral lesion usually flat, or rectangular, from the stocks.
Many different types of torsions spring are available in automated machinery, with applications ranging from clocks and clocks to motion control.
#3. Extension Springs
Expansion springs are helically coiled wires, which are designed to provide an opposing force when stretched. Key specifications include spring rate, helix type, spring end type, wire diameter, material, and free and maximum extended length.
Extension springs are mainly used in manufacturing applications where a variable, opposing force is required between two components. Materials are available based on several sizes, spring rates, and required available forces. The end a usually formed in the shape of a hook or loop & can also be custom-made.
A variety of spring ends are used with extension springs, and many of these are standardized for specific applications, typically formed in the shape of a hook or loop, and can also be custom made.
#4. Constant Force Springs
Clocks have clock springs or constants force springs. A constant force spring is a tightly wound band of steel that resembles a roll of tape. A load forces the springs to contract, & when it is removed, the spring rebels with constant forces. Constant force spring is also found in wind-up toys and similar devices.
#5. Drawbar Springs
Drawbar springs are coil compression springs, including U-shaped wire forms, inserted for use in extension applications. The drawbar spring combines the application of tension of the extension spring with the positive stop feature of the compressions spring.
Key features include free length, maximum spring deflection, and wire diameter. Drawbar springs are mainly used in applications where a tension-producing spring is required, where the self-limiting feature of compression springs is also required.
A typical use for drawer spring supports porch swings, where the spring cannot be loaded from the point of failure dues to the self-limiting property of the compression springs.
Also, Read: What Is a Gear Pump? | Components of Gear Pumps | Types of Gear Pump | Working of Gear Pump
#6. Volute Springs
Volute springs are wound flat metal strips together, forming helical spirals that are commonly used in compression applications. Key features include the intended application, diameter, stroke, material, and final attachment style.
Volute springs are mainly used in applications where a compression spring is required for a long fatigue life or a repetition of high spring force. They come in different sizes depending on applications & force, and materials.
Some solute springs are single-ended, while others are double. An easily recognizable use of solute spring is the compression spring found in high-quality nail clippers or pruning shears.
#7. Garter Springs
Garter springs are spring coils whose ends join to form spherical springs that are used to provide a radial force to components that may have a variable load. A common use of garters springs is in hydraulic, pneumatic, & radial shaft seals, where they provide a slight inward force on the sealing lips.
#8. Flat Springs
Flat springs are strips or metal straps, or assemblies of such type, that are made to form a repeating counterforce when compressed or displaced and used for positioning or contact. Key features include the intended application, flat spring type, and spring and type.
Flat springs are mainly used in applications where a repetitive counterforce is required to control the speed or load by applying contact and force. They are available in various sizes, types, materials, as well as mounting types or sizes. Some easily identified examples of flat springs are the imbalance in flat battery contacts, vehicle leaf springs, and sliding screen windows.
Also, Read: What Are Cutting Fluids? | Types of Cutting Fluids | Uses of Cutting Fluids | Selection of Cutting Fluid
#9. Gas Springs
Gas springs are mechanical devices consists of a cylinder and a rod, which use pressure from the pre-charge of nitrogen, or other inert gases, to create a force bias on the piston or rod. Key features include intended application, stroke, compressed length, extended length, force, as well as features.
Gas springs are mainly used in the automobile industry to lift and/or reduce the hood or hatch. They are available in various sizes and stroke lengths depending on the application & load requirements. Others applications include use on office chairs for seat height adjustment.
#10. Air Springs
Air springs are air pressure pressures or bladder-type devices of various sizes and shapes and are used to provide activation, shock absorption, and vibration isolation. Key features include the intended application, type, style, physical dimensions, mounting type as well as features.
Air springs are mainly used in machine applications such as vehicle suspensions for shock absorption and as machine mounts for vibration isolation. They are available in various types & sizes depending on load requirements and application. Other uses include lifting, compressing, bending, etc. Air spring used for vibration isolation is also known as air cushions.
#11. Other Springs
Springs that are assembled into components for special applications are called spring assemblies. The springs used to protect the hydraulic line are called protective coil springs. Hydraulic springs use specials hydraulics fluid in very short stroke applications and are found in die springs.
#12. Leaf Springs
It is an arc-shaped spring, made up of strips of metal one after the other and held together using a nut and bolt or clamps. It is a widely used suspension system for commercial vehicles such as buses, trucks, etc. This spring is capable of withstanding large forces in small areas. It is usually made of steel, graphite epoxy, carbon epoxy.
#13. Special Purpose Springs
Air spring, gas spring, extension spring, greater spring, etc., fall under the category of special purpose springs. As the name implies, “special purpose,” meaning that these springs are not widely used, but still in some cases like vice-grip pliers, carburetor, trampoline, washing device, even We also use extension spring in toys.
Nowadays, we use an air spring, where the air is used to pump the bladder, which helps us to absorb shock and vibration completely. So these types of springs fall under the category of special purpose springs.
Also, Read: What Is Normalizing Process? | Normalizing Process Procedure | Purpose of Normalizing Process
Spring Materials:
Springs are made of the following materials:
- Hard draw wires:- These are general purpose springs, where we require low-temperature resistance and low tension; we can use these types of spring materials.
- Graphite epoxy:- It is used in high-strength springs such as leaf springs.
- Carbon epoxy:- It is made of carbon fiber and has a high load-bearing capacity; this material is also used in high-power applications such as automobiles and locomotives.
- Stainless steel:- Nowadays, stainless steel is widely used in the manufacture of spring.
- Phosphor Bronze:- This type of spring is used in the electrical industry because the material has good electrical conductivity & good resistance to corrosion.
- Chrome Silicon:- These types of springs can be used in high temperatures up to 250 ° C.
- Chrome Vanadium:- This type of spring has good thermal conductivity up to 220 ° C and also has good fatigue resistance.
Application of Spring in Mechanical:
Springs are used in the following areas:-
- Automobile suspension system.
- In cam-follower assembly, we also use spring.
- Spring is used in railway bogies.
- We used spring in the clutches, brake, & valve assembly to apply force to these objects.
- Springs are used in garage doors, gardenings equipment, door locks, and many other household items.
Advantages of Spring in Mechanical:
These are the following advantages of spring:
- Produce a good cushion effect.
- The spring has a good shock-absorbing ability.
- It has high durability.
- The spring has the potential for energy stored inside it.
- It is easy to design and cheap to produce.
- Spring is a maintenance-free device.
Disadvantages of Spring in Mechanical:
It has the following disadvantages in the spring:
- Its loose shape and stability from day Today.
- Sometimes, when the axial loads of the spring increase, it produces a buckling event.
- If the spring is broken, it is difficult to repair.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Different Kinds of Springs
Different types of springs: compression, extension, torsion, & constant force springs.
Types of Spring
Compression Springs; Extension Springs; Torsion Springs; Constant Force Springs; Belleville Springs; Drawbar Springs; Volute Springs; Garter Springs.
Different Spring Types
The most common spring types include:
- Compression Springs.
- Extension Springs.
- Torsion Springs.
- Constant Force Springs.
- Belleville Springs.
- Drawbar Springs.
- Volute Springs.
- Garter Springs.
- Flat Springs
- Gas Springs
- Air Springs
Mechanical Spring
A metal wire spring that functions in a spring mechanism that compresses, extends, rotates, slides, pulls, and exerts force when an equal or greater force is applied. A spring mechanism can exert pressure, rotational force, or pulling strength in a variety of ways.
Drawbar Springs
Drawbar springs are compression springs that are excellent for use in potential overload situations and offer a built-in safety feature that, upon fracturing, will continue to carry a static load.
Spring Materials
spring materials · High Carbon Steels · Stainless Steels · Alloy Steels · Composite · Copper Alloys · Nickel Alloys.
Types of Springs in Mechanical Systems
Different types of springs: compression, extension, torsion, & constant force springs. Two of the most common types of springs are compression and extension springs. These helical mechanisms are most often made of metal, but occasionally are made of other materials as well.
Spring Design and Calculations in Mechanical Engineering
Spring design and calculations in mechanical engineering involve determining the appropriate parameters for designing and selecting springs for various applications. Here are some key aspects to consider:
- Spring Types:
- Compression Springs: These springs are designed to resist compression forces and are typically used in applications where the spring is compressed to store energy or provide resistance.
- Extension Springs: Extension springs are designed to resist pulling forces. They expand when pulled and are commonly used in applications where the spring needs to extend or pull back a load.
- Torsion Springs: Torsion springs apply torque to resist rotational forces. They are used in applications where the spring needs to rotate and provide torsional resistance.
- Spring Constants:
- Spring Rate (k): The spring rate determines the relationship between the applied force and the deflection of the spring. It is calculated as the force required to deflect the spring by a unit distance (e.g., pounds per inch or Newtons per millimeter).
- Spring Constant (k): The spring constant is the reciprocal of the spring rate and represents the stiffness of the spring.
- Material Selection:
- Springs are typically made from materials with high strength and good elastic properties, such as steel alloys. The material choice depends on factors like load requirements, operating conditions (temperature, corrosive environments), and cost considerations.
- Deflection and Stress:
- Deflection: Deflection is the amount of deformation experienced by a spring under an applied load. Calculating deflection helps determine if the spring will provide the required displacement or compression.
- Stress: Stress analysis ensures that the spring material remains within its elastic limits, preventing permanent deformation or failure. Stress calculations involve factors such as wire diameter, coil diameter, and the applied load.
Spring Materials and Their Properties in Mechanical Applications
An ideal spring material has high strength properties, a high elastic limit and a low modulus. Because springs are resilient structures designed to undergo large deflections, spring materials must have properties of extensive elastic range.
Spring Manufacturing Companies in the USA
There are numerous spring manufacturing companies in the USA that specialize in producing a wide range of springs for various applications. Here are a few well-known spring manufacturers:
- Associated Spring (Barnes Group Inc.): Associated Spring is a prominent manufacturer of springs and spring products. They offer a comprehensive range of springs, including compression, extension, torsion, and flat springs. They serve diverse industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical, and industrial.
- Lee Spring Company: Lee Spring is a leading supplier of stock and custom springs. They provide a vast selection of springs, including compression, extension, torsion, wave, Belleville, and constant force springs. They cater to industries such as electronics, telecommunications, automotive, and medical.
- Peterson Spring: Peterson Spring is a family-owned company with extensive experience in spring manufacturing. They offer a wide range of springs, including compression, extension, torsion, and wire forms. They serve industries like automotive, agriculture, aerospace, and industrial.
- Katy Spring & Mfg., Inc.: Katy Spring is a custom spring manufacturer based in Texas. They produce various types of springs, including compression, extension, torsion, and wire forms, tailored to specific customer requirements. They cater to industries such as oil and gas, automotive, medical, and construction.
- M & S Spring Company: M & S Spring specializes in custom spring manufacturing and prototyping. They manufacture a wide range of springs, wire forms, and stampings for industries such as automotive, aerospace, defense, and electronics.
Importance of Proper Spring Selection for Mechanical Systems
Proper spring selection is crucial for mechanical systems for several reasons:
- Load Handling: Springs are often used to support or apply loads in mechanical systems. Choosing the right spring with the appropriate load-bearing capacity ensures that the spring can effectively handle and distribute the applied load. Improper spring selection may result in premature failure, reduced performance, or safety hazards.
- Functionality and Performance: Springs play a vital role in achieving the desired functionality and performance of mechanical systems. For example, in automotive suspension systems, selecting the correct springs helps maintain proper ride height, control vehicle dynamics, and provide optimal comfort and handling. Inaccurate spring selection can lead to poor performance, instability, or compromised functionality.
- Deflection and Stiffness: Springs exhibit specific deflection characteristics and stiffness properties. Proper spring selection ensures that the spring can achieve the required deflection or compression based on the system’s design requirements. The stiffness of the spring should match the intended application, whether it’s providing support, absorbing shocks, or exerting a specific force.
- Dynamic Response: In dynamic systems, such as oscillating or vibrating mechanisms, springs are critical in controlling and managing the dynamic response. Selecting springs with appropriate natural frequencies and damping characteristics helps maintain stability, prevent resonance, and reduce unwanted vibrations or oscillations.
- Safety and Reliability: The proper selection of springs is essential for ensuring the safety and reliability of mechanical systems. By choosing springs with adequate strength, durability, and fatigue resistance, the risk of spring failure or malfunction can be minimized, reducing the chances of accidents or system breakdowns.
What Is Spring in Mechanical Engineering?
A spring is an elastic object that stores mechanical energy and releases it when the opposing force is removed. If you need to apply force to create movement or hold something in place without the use of engines or other powered means, springs could be the answer.
Spring in Mechanical Engineering
What Is a Spring? A spring is an elastic object that stores mechanical energy and releases it when the opposing force is removed. If you need to apply force to create movement or hold something in place without the use of engines or other powered means, springs could be the answer.
Types of Spring in Mechanical Engineering
What are the 3 types of springs? There are three main types of springs are the helical springs, disk springs, and leaf springs. Each main type has different types of springs under it. For example, the helical springs consist of the torsion spring, extension spring, spiral spring, and compression spring.
Applications of Spring
Springs change their shape when force is applied and regains their original position when we remove it. We use many products in our day-to-day life that use springs to achieve the required function. For example, springs are used in analog watches, bicycles, cars, and toys to store mechanical energy and release it.
Mechanical Spring Types
- Step 1: Compression Spring. A compression spring squeezes together to create a load.
- Step 2: Extension Spring.
- Step 3: Torsion Spring.
- Step 4: Constant Force Spring 1.
- Step 5: Constant Force Spring 2.
- Step 6: Belleville Spring (aka Belleville Washer)
- Step 7: Spring Clip.
- Step 8: Natural Spring.
Mechanical Types
- Acoustical Engineering.
- Aerospace Engineering.
- Automotive Engineering.
- Mechanical Engineering.
- Mechatronics Engineering.
- Railway Engineering.
Spring Mechanism Examples
The most common use for a spring is to return a mechanism to its starting position and/or to add cushioning. Examples of applications that use springs include firearms (triggers), mouse traps, trampolines and car suspensions.
Coil Spring
A coil spring is a helical-shaped mechanical device that is close-wound or open-wound. Coil springs store mechanical potential energy. They can be made of elastic materials or metal such as hardened steel. You can find coiled springs in many ordinary items—from farm equipment to toys, trampolines and much more.
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –
- Types of Dial
- Cutting Fluids
- Kinds of Engines
- Gear Type Pump
- Parts of Disc Brakes
- Normalizing Process
- Resistance Projection Welding
- Different Types of Cooling Tower
- Chip Thickness Ratio | Shear Angle of Chip Thickness Ratio
- Resistance Projection Welding | Working of Resistance Projection Welding
- Parts of Turret Lathe | Working of Turret Lathe | Types of Turret Lathe | Advantages of Turret Lathe
- Techniques of Gas Welding | Parts of Welding Torch | Working of Gas Welding | Types of Gas Welding | Types of Flames in Gas Welding
- Parts of Reciprocating Pump | Definition of Reciprocating Pump | Working of Reciprocating Pump | Mathematical Analysis of Reciprocating Pump