Important Point
What Is Laser Beam Machining?
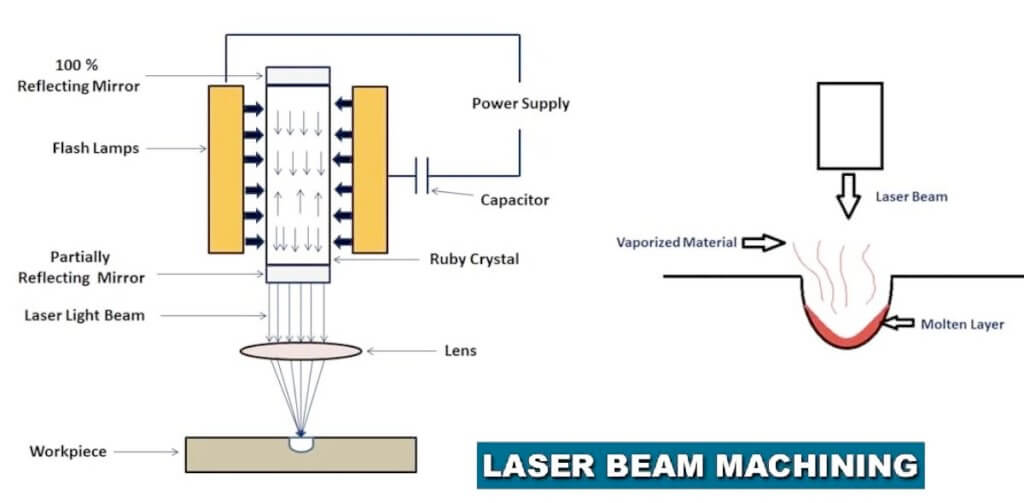
- A laser beam machining is a non-traditional machining method in which the operation is performed by laser light.
- The laser light has a maximum temperature on the workpiece, causing the workpiece to melt due to the high speed.
- The process used thermal energy to remove material from a metal surface.
- Laser beam machining is a form of the machining process in which laser beams are used for the Machinings of metal and non-metallic materials.
- In this process, laser beams of high energy are created to strike the workpiece, and the thermal energy of the lasers is transferred to the surface of the W/P (workpiece).
- The heat generated on the surface heats melts and vaporizes the material by w / p.Light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation called Laser.
Working Principle of Laser Beam Machining:
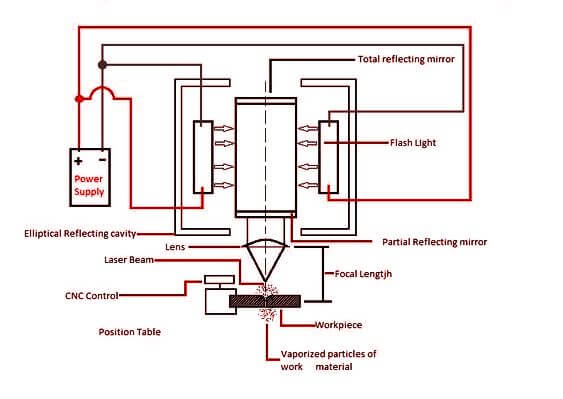
- A very high-energy laser beam is produced by laser machines.
- Focuses on the workpiece to mechanize this laser beam produced.
- When the laser beam hits the surfaces of the W/P, the thermal energy of the laser beam is transferred to the surfaces of the W/P.
- It heats, melts, evaporates, and eventually makes the material a workpiece.
- This is how laser beam machining works.
- It works on the principle that when a high-energy laser beam strikes the surfaces of the workpiece.
- The heat energy contained by the laser beams is transferred to the surface of the w/p.
- This heat energy absorbed by surface heat melts and evaporates the material w/p. Machining of materials in this way is done using laser beams.
Advantages of Laser Beam Machining:
- The Following Advantages of Laser Beam Machining Are:
- It can be focused on very small diameters. It produces a huge amount of energy, about 100 MW per square mm area.
- It is capable of producing a very accurately placed hole.
- Laser beam machinings have the ability to cut or engrave almost all types of materials when conventional machining processes fail to cut or engrave any material.
- There is no physical contact between the equipment and the workpiece.
- The wear and tear in this machinings process are very low and therefore requires a low maintenance cost. This machining process produces an object of very high precision.
- And most items do not require additional finishing; They can be combined with gases that help make the cutting process more efficient.
- This helps reduce oxidation of the W / P surface and keep it free of melting of the vaporized material.
- It has the ability to engraves or cut almost all types of material. But it is best suited for brittle materials with low conductivity.
Also, Read: Parts of Shaper Machine | What Is the Shaper Machine? | Working of Shaper Machine
Disadvantages of Laser Beam Machining:
- High initial cost. This is because it requires many accessories that are important to the machining process by Laser.
- Laser beam machining requires a highly trained worker to operate the machine.
- Low production rate because it is not designed for mass production.
- The machining process requires a lot of energy. It is not easy to produce deeps cuts with w / p that have high melting points and usually cause a cone.
Application of Laser Beam Machining:
- Laser beam machining is mostly used in the automobile, aerospace, shipbuilding, electronics, steel, and medical industries for precision machining complex parts.
- In heavy manufacturing industries, it is used or used for drillings and claddings, seam and spot weldings, among others.
- In light manufacturing industries, it is used for engravings and drilling other metals.
- In the electronics industry, it is used for circuiting and wire stripping (for connecting the two ends).
- In the medical industry, it is used for hair removal and cosmetic surgery.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What Is Laser Beam Machining?
Laser Beam Machining (LBM) is a form of processing that uses direct heat from a laser beam. This process uses thermal energy to remove material from metallic or non-metallic surfaces.
Laser Beam Cutting Machine
Laser cutting is a technology that uses a laser to vaporize materials, resulting in a cut edge. Although normally used for industrial manufacturing applications, it is now used by schools, small businesses, architecture, and hobbyists.
Beam Laser Cutter
A powerful laser cutter and engraver that allows you to model, cut, and engrave on materials such as wood, leather, acrylic, and cardboard.
Laser Beam Machining Process Can Be Used For
Lasers can be used for welding, cladding, marking, surface treatment, drilling, and cutting, among other manufacturing processes. It is used in the automobile, shipbuilding, aerospace, steel, electronics, and medical industries for the precision machining of complex parts.
Laser Beam Machining Process
Laser beam machining is a form of the machining process in which laser beams are used for the Machinings of metal and non-metallic materials. In this process, laser beams of high energy are created to strike the workpiece, and the thermal energy of the lasers is transferred to the surface of the W/P (workpiece).
Working of Laser Beam Machining
Focuses on the workpiece to mechanize this laser beam produced. When the laser beam hits the surfaces of the W/P, the thermal energy of the laser beam is transferred to the surfaces of the W/P. It heats, melts, evaporates, and eventually makes the material a workpiece.
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –
- Difference Between Orthogonal and Oblique Cutting | Orthogonal Machining
- Parts of Shaper Machine | What Is the Shaper Machine? | Working of Shaper Machine
- What Is a Synchromesh Gearbox? | Principle of Synchromesh Gearbox | Construction of Synchromesh Gearbox | Working of Synchromesh Gearbox
- Working of Constant Mesh Gearbox | What Is a Constant Mesh Gearbox? | Different Gear Ratios in Constant Mesh Gearbox | Construction of Constant Mesh Gearbox
- What Is Magneto Ignition System | How Does an Ignition System Work | How Does a Magneto Work | What Does a Magneto Do | Magneto Ignition System