Important Point
What Is Inverter Generator?
An inverters generator is a new type of powers sources that have becomes very popular in recent years because it generates clean, stable AC power without any sound-proof enclosures. This can set this model to output 120 V or 240 V, and, as you can imagine, they are much quieter than traditional generators.
Many times you must have heard that inverter generators are fuel-efficient and quieter than conventional generators. Have you wondered why this is so? Well, today, we are going to answers all your questions regarding the inverter generator, so keep reading. Before that, you need to understand how an alternator works.
Alternators are almost the same as a generator, but there is one major difference. In an alternator, the rotor is excited by a DC current, and thus a strong magnetic field is generated by the rotor. And when the rotors rotate, the stators cut off these magnetic fields, and hence electricity is generated, which is collected through the stator.
But in the case of the generator, armature winding rotates in a certain magnetic field, and the stator produces these magnetics fields with the help of excitation winding.
How Does an Inverter Generator Work?
The mechanics of an inverter generator are a bit more complicated than that of a traditional portable generator. More parts are involved in delivering the final power output. Many inverters generators also run on fossils fuels.
In addition to the power being drawn from the fuel tank, the inverter generator also contains the battery, alternator, and inverter. The power coming out of the engine is a high-frequency AC current which is converted into DC current by the alternator.
Those DC currents are then converted backs into AC current by the inverter. Like traditional portable generators, inverter generators also have an output of 120 volts at 60 Hz. However, due to the additional steps in power generation, the current of an inverter generator is much more constant.
In other words, there are fewer harmonics distortions, which is why inverter generators are said to produce ‘clean electricity. The quality of electricity produced by the inverter generator is equal to the quality of electricity that you get from the main electricity supplier.
Clean electricity is possible for two reasons. The first factors are that the initial AC current in the inverter generator is at a higher frequency which gives more electrical energy. The second factor is the conversion of DC current back to AC current.
The mechanics of an inverter generator have more control over the AC frequency, which allows it to provide a very stable sine wave. Greater control over power output makes inverter generators quite energy-efficient.
It can adjust its voltage as necessary for the connected load while maintaining an RPM of 3600. Steady current is also one of the main reasons why inverter generators are significantly quieter than traditional portable generators.
Also, Read: What Are Resistors? | Resistance with a Sinusoidal Supply | What Is Impedance? | Resistance VS Impedance
How did an Inverter work?

An inverter takes the power that comes in the form of a direct current and converts it into an alternating current. It accomplishes this by sending current within the sending switch in different directions. Filters can then be applied to smooth the waveform and give it a solid frequency.
Power inverters are surprisingly popular today due to their size and, to some extent, efficiency. Different types of inverters use different filtering methods, depending on how smooth the output needs to be. Devices called rectifiers are used to converts AC power into DC.
One of the most popular everyday uses of inverters is to produce electricity to run various electronics in automobiles. Cars generally produce DC, which is not in harmony with most appliances to use regular home outlets.
Recent cars have an accessory port into which a compact inverter can be plugged, enabling cell phones, small TVs, or other electronic devices to use power. Some small inverters are intended to be plugged into a car’s cigarette lighter.
Large inverters are installed on construction sites to deliver power for power tools and other equipment. Solar and wind power generators use inverters to convert the electricity they produce to be applied to the home.
An essential difference between an inverter and a generator, namely generator vs. inverter, an inverter can only work if there is a source of electrical energy first; It cannot produce its own.
Unless part of a combination machine, inverters only convert DC to AC, whereas a conventional generator cannot convert the current from one form to another.
How did a Generator work?

The generators are the device that converts mechanical energy into electricity. In most cases, power generators are capable of providing energy to a home. Large-scale electric generators may be powered by natural gas, coal, or nuclear power.
A portable generator uses regular gasoline or diesel fuel to generate electricity for use during power outages in a construction location or building. Generators can be tuned to produce either AC or DC electricity, although most power stations and small applications produce AC.
This is all conventional generators do, although they generate electricity. For example, if the voltage that power is required, for example, a transformer should be employed.
Inverter Generators:
Inverter generators are similar to conventional generators as they generate AC power which is then converted to DC power before converting to AC. It provides a smoother, more continuous flow of power. The conversion enables the generator to be more fuel-efficient as well as perform more quietly than regular models.
Power Converters:
Some confuse an inverter with a power converter, even applying the terms to the contrary. A converter is used to convert the voltage from one level to another.
Differents voltages levels are used in different countries, & travelers in other parts of the world may need a converter to use appliances such as electric shavers and hairdryers.
Generator VS Inverter:
| Principle | Diesels-Run Generators (DG) | Inverters |
| Storage | The generators do not store electricity; As the name suggests, it generates electricity once started. Therefore, it needs to be started firsts, and only then will it provides power. Obviously, there will be time lags between starting & receiving backups power afters the utility supplies fails. | A power inverter set stores power in the form of direct current (DC) in the batteries. It firsts converts the mains to alternating current (AC) during charging & stores it; Quickly switches it to AC to power your appliances. There are no time intervals; No manuals start either. |
| Energy | A generator produces electricity. It is the mechanical device that converts the calorific values of gallons of diesel into electricals energies using rotating devices. | An inverter simply stores and re-converts energy. When DC powers are reversed into AC electricity, the result is an inductive electricals signal. Properly filtered, it has the same properties as a full alternating current. |
| Weight | Unless your power backup needs are small (home lighting and home appliances only), a DG set can be bulky and bulky, requiring a metal frame and wheels. Technically, they are portable, but they lack the convenience factor. | An inverter isn’t a bulky, bulky device, but it only works with a set of connected batteries. These can be heavy and are not easy to shift around. |
Also, Read: What Is Piston Ring? | How Is Piston Ring Installation Done? | Types and Functions of Piston Rings
What Is the Difference Between Ac And Dc Current?
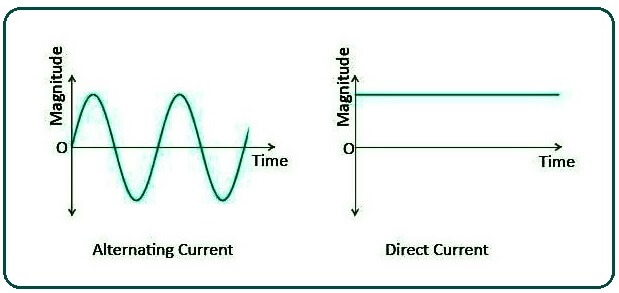
Alternating current & direct currents differ in that electrons flow back & forth in AC, but only in one direction in DC. Because AC can tolerate more voltage, it loses less energy over long-distance progression.
As a result, AC is commonly used to supply power in most homes and buildings. Hence most home appliances run on AC; Conversely, they must convert the AC power supplied to the building or house into DC to power the device.
Personal computers typically run on DC and include a rectifier to perform this conversion. In this case, the rectifier is referred to as a regular power supply.
Also, Read: What Is Biomass? | Different Method of Biomass Conversion | Method of Biomass Conversion
Difference Between Inverter Generator and Conventional Generator:
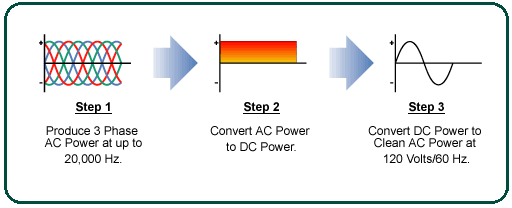
The conventional generator or non-inverter generator produces AC current directly, while the inverter generator produces AC current, then converts it into DC current and then converts it back into AC current, and has many advantages regarding We will discuss later. An inverter generator is also fuel-efficient; Let us understand it with this equation.

This is the equation for the rotor speed of the generator, and all generators, including inverter generators, alternators, and conventional generators, produce power based on this equation.
Countries like the US and Canada use 60Hz frequency, so here f=60 and P are the number poles of a particular generator. Almost all generators except those used in hydropower have two-pole arrangements. Now, as you know, the frequencies of the currents should be 60Hz, and if the frequency fluctuates even a bit, say 58Hz or 61Hz, it can damage your equipment.
If we do simple math, to get f=60, the value of n must be 3600 RPM (rotations per minute). This means that the generator rotor must be running at 3600 RPM continuously, no matter what.
And if this speed increases or decreases, it can change the frequency of the output current.
So now, you know that a conventional generator must run continuously at 3600 RPM, no matter how much power is demanded.
Let us understand it with these examples. Suppose you have generators that can supply 1000 watts of continuous powers, not peak powers, & you want to run a 100-watt bulb. So it will burn some fuel, right? Now let’s say he wants to run a 500-watt electronic device. In both cases, the generator will, of course, consume fuel, but in both cases, the generator must run at 3600 RPM to produce a 60Hz current.
So as you can see, there’s are definitely a waste of fuel; Not that much, but some amount of fuel goes to waste. Well, now let’s understand the inverter generator. As I said earlier, the inverter generator generates electricity in three phases; First, it produces AC power, then converts it into DC power, and then again converts it into AC power.
These are especially helpful when you need fewer powers from an inverter generator because the generator will spin at a lower speed (lower fuel consumption) and produce electricity with a lower frequency. Then the rectifier will convert it into DC power, and then the inverter circuit will convert it into 120V 60Hz power.
Let us understand it with this example. Suppose you have inverter generators that can supply 1000 watts continuously, & you want to run a 100-watts bulb. & then you want to run 500-watt devices on it. Now in the cases of a 100-watt bulb, the inverter’s generators will burn fewer fuels than a conventional generator since it does not need to produce a 60Hz supply; therefore, the rotation speed will be much lower. And in the case of 500-watt devices, the rotors will rotate less than 3600 rpm accordingly to produce the required power.
When to Choose an Inverter Generator:
The advantages of inverter generators over traditional portable generators are that they are quieter, more compact and lighter, more fuel-efficient, safer for sensitive electrical equipment, and generally more environmentally friendly.
The disadvantages of an inverters generator are that they are usually more expensive than a comparable conventional generator and do not have as much power. Given these advantages and disadvantages, an inverter generator is more suitable for occasional use and especially for outdoor activities like camping.
An inverter generator is a great option when you don’t need a lot of electricity but need convenient, clean electricity that is easy to carry with you.
Also, Read: What Is Solar Energy Used For? | What Is Good About Solar Energy? | Fun Facts About Solar Energy
Diesel-Run Generator Disadvantages:
- Highers maintenance costs in the long run due to wear and tear of moving parts
- high noise output
- High pollution due to the use of fossil fuels
- High operating costs due to the ever-increasing cost of diesel and relatively low efficiency
- The inconvenience of refueling and storage
- Fire hazard of diesel storage – requires installation away from the place of use.
- It runs at the same speed of 3600 RPM, so you can expect similar noise even when less equipment is connected. Its cost is also high when the load requirements are low.
- No compatibility with solar panels
Also, Read: Types of Measuring Instruments
Inverter Advantages:
- An inverter is safe for electronic devices and other sensitive devices such as computers and personal printers. This produces a pure sine-wave output that matches the quality of the main supply.
- It provides backup critical, for doctor’s clinic without interruption, without any inconvenience, and without starting time.
- hardly makes any noise
- Doesn’t pollute – eco-friendly
- Greater efficiency of operation hence lower running cost
- Backup time is inversely proportional to load. The lower the load, the longer the backup time.
- Next-generation inverters are designed for solar compatibility, so you can use solar power to generate electricity or run appliances, or even charge batteries.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How Does an Inverter Generator Work?
An inverter generator works by converting AC electric current into DC electric current and then inverting it back to AC to create a cleaner wave of electricity. If you’re not sure what the difference between AC and DC power is, please check out our article about electrical phases.
How Does an Inverter Work?
An inverter converts the DC electricity from sources such as batteries or fuel cells to AC electricity. The electricity can be at any required voltage; in particular, it can operate AC equipment designed for mains operation or rectified to produce DC at any desired voltage.
What Is Inverter?
An inverter provides an ac voltage from dc power sources and is useful in power electronics and electrical equipment rated at the ac mains voltage. In addition, they are widely used in the switched-mode power supply inverting stages.
Portable Generator Vs. Inverter Generator
On a conventional portable generator, the engine speed is fixed—typically at 3600 RPM—and always runs at that speed. A portable inverter generator varies its speed to produce the power required. Turn on a few lights, and the engine speed increases. Turn them off again, and the engine slows down.
What Is the Difference Between Inverter Generator and Regular Generator?
Conventional generators use a mechanical alternator to produce alternating current (or AC) power that’s ready to use. Inverter generators also use an alternator to produce AC power, but this current is converted into direct current (or DC) before a microprocessor inverts it back into cleaner AC power.
What Is Inverter Generator?
An inverter generator electronically throttles the engine up and down to meet demand instead of running full tilt all the time. The resulting improvement in efficiency means that you won’t have to fill up the gas tank as often. Inverter generators also produce lower emissions and are generally very quiet.
Inverter Vs. Generator
Generators are complex, heavy-load devices with large capacities that use mechanical energy from external sources and convert them into electrical energy, and they produce electrical power. Inverters are low-power devices that draw power from a fixed DC source and use a microprocessor to convert DC power into AC power.
Inverter Generator How It Works
An inverter generator works differently. The alternating current (AC) power produced by the alternator is sent to a rectifier, which is a device that converts the AC power to direct current (DC). This DC power is then inverted back to AC power by the computer inside the generator before it is sent to the control panel.
Advantages of Inverter Generator
- High-quality power output.
- Other generator design.
- Lighter, smaller size.
- Higher fuel efficiency.
- Quiet operation.
- Parallel capability.
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –
- Parts of a Solar Panel
- Difference Between Orthogonal and Oblique Cutting | Orthogonal Machining
- Parts of Shaper Machine | What Is the Shaper Machine? | Working of Shaper Machine
- What Is a Synchromesh Gearbox? | Principle of Synchromesh Gearbox | Construction of Synchromesh Gearbox | Working of Synchromesh Gearbox
- Working of Constant Mesh Gearbox | What Is a Constant Mesh Gearbox? | Different Gear Ratios in Constant Mesh Gearbox | Construction of Constant Mesh Gearbox
- What Is Magneto Ignition System | How Does an Ignition System Work | How Does a Magneto Work | What Does a Magneto Do | Magneto Ignition System